The Indo-Europeans, also known as the Proto-Indo-Europeans (PIE), represent one of the most enigmatic and influential peoples of ancient times. Their legacy is woven into the fabric of numerous modern languages, cultures, and civilisations, spanning vast regions from Europe to parts of Asia. Let’s delve into the origins, culture, and impact of these ancient peoples.
Origins and Migration
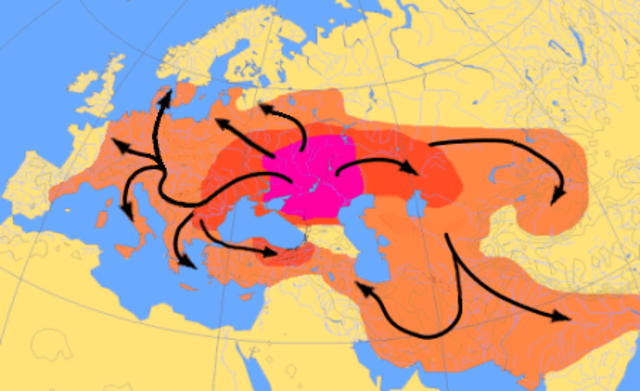
The Indo-Europeans are believed to have emerged around the 4th millennium BCE. However, pinpointing their exact homeland remains a subject of scholarly debate. The most widely accepted theory places their origins in the Pontic-Caspian steppe region. This area encompasses parts of present-day Ukraine and southern Russia.
From this homeland, the Indo-Europeans embarked on a series of migrations and expansions that shaped the cultural and linguistic landscape of Eurasia. They dispersed in multiple waves, spreading across Europe, Central Asia, and the Indian subcontinent. These migrations played a crucial role in the formation of numerous ancient and modern civilisations.
Language and Linguistic Legacy
Perhaps the most significant contribution of the Indo-Europeans is their language. The reconstructed Proto-Indo-European language serves as the theoretical ancestor of a vast linguistic family known as the Indo-European language family. This linguistic group includes languages such as Latin, Greek, Sanskrit, Persian, Germanic, Celtic, Slavic, and many others.
The spread of Indo-European languages facilitated communication, trade, and cultural exchange among diverse peoples. It laid the groundwork for the development of literature, philosophy, law, and science in numerous ancient societies. The Indo-European linguistic legacy continues to shape global communication and cultural exchange in the modern world.
Society and Culture
The social and cultural practices of the Indo-Europeans are gleaned from linguistic evidence, archaeological findings, and comparative studies of ancient civilizations. They were predominantly pastoralists, relying on animal husbandry for sustenance and mobility across the vast steppes.
Indo-European society was hierarchical, with a class structure that included rulers, warriors, priests, and commoners. Religion played a central role in their lives, reflected in the worship of deities associated with natural phenomena, celestial bodies, and cosmic forces. The Indo-Europeans also held elaborate burial rites and practiced ritual sacrifices to honor their ancestors and appease the gods.

Legacy and Influence
The legacy of the Indo-Europeans reverberates through the corridors of history, leaving an indelible mark on the cultures and civilizations that followed. Their linguistic heritage continues to shape the world’s most spoken languages, fostering connections and shared cultural identities across continents.
Moreover, the Indo-European migrations and interactions contributed to the diffusion of ideas, technologies, and cultural practices throughout Eurasia. From the foundations of classical civilisations in Greece and Rome to the emergence of medieval kingdoms in Europe and the development of ancient Indian and Iranian cultures, the Indo-Europeans played a pivotal role in shaping the course of human history.
The Indo-Europeans stand as a testament to the enduring impact of ancient peoples on the tapestry of human civilization. Their migrations, languages, and cultural practices have left an undeniable imprint on the world, shaping the course of history and enriching the diverse mosaic of global cultures. As we unravel the mysteries of the past, the story of the Indo-Europeans reminds us of the interconnectedness and shared heritage of humanity across time and space.

